

- #Determination of intrinsic viscosity of polymers verification
- #Determination of intrinsic viscosity of polymers iso
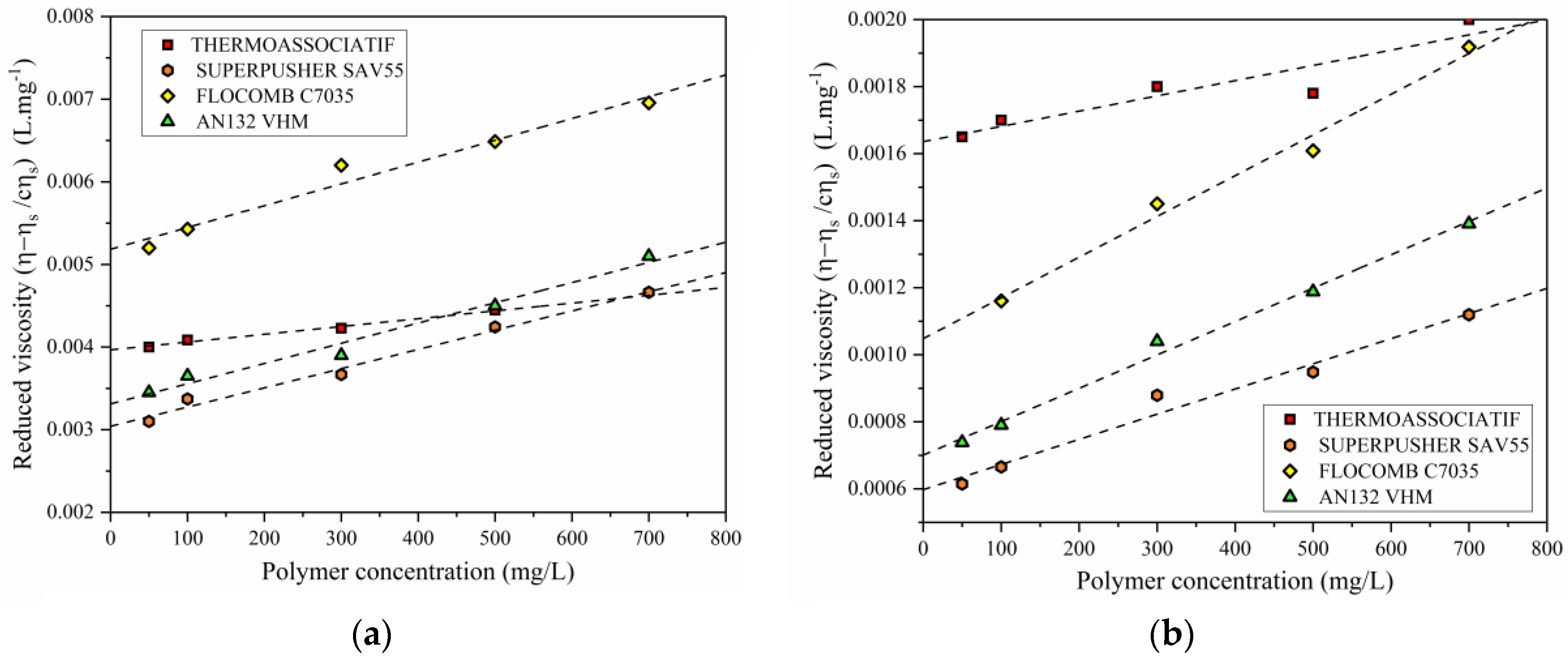
The value of 1.21 indicates that the cellulose molecules dissolve in THDS quite well. The relationship between the molecular weight of cellulose and the intrinsic viscosity tested in such dilute solutions has been established in the form of the Mark–Houwink equation, = 0.24 × DP 1.21. That is to say, the cellulose was dissolved in the solution in molecular level, and the viscosity of the solution is linearly dependent on the concentration of cellulose. In this work, tetra-n-butylammonium hydroxide (TBAH) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) aqueous solution (THDS) were used to dissolve cellulose in a few minutes under room temperature into true molecular solutions.
#Determination of intrinsic viscosity of polymers iso
This characteristic is included in some product standards, such as ISO 7823, which is being applied for the characterization of methacrylate (PMMA) screens such as those used for protection and safety against COVID-19.ĪIMPLAS has an automatic viscosimeter and a vast experience in determining the viscosity of polymers in solution.ĭo not hesitate in contacting us if you have any doubt related to this subject.The determination of molecular weight of natural cellulose remains a challenge nowadays, due to the difficulty in dissolving cellulose. This test is normally used to characterize PET used in bottles, sheets or fibres polyamides in automotive parts or technical parts and PVC used in sanitation pipes.įor each polymer, there are preferential ways to express the result of the viscosity measurement: intrinsic viscosity for PET viscosity for polyamides K value for PVC. In the case of highly diluted solutions (c <<), it can be assumed that the viscosity ratio between the solution and the solvent is equal to the ratio between their flow times in the capillary. The viscosity will be determined by the ratio between the flow time of the polymer solution (t) and the flow time of the pure solvent (t 0). Both the net solvent and the polymer solution flow through the capillary and the flow times are recorded. The test consists of dissolving the polymer in a suitable solvent at very low concentration (c). The measurement of the viscosity is described in UNE-EN ISO 1628 and UNE-EN ISO 307 using Ubbelohde-type glass capillary viscometers. The molecular weight is an essential characteristic that determines some mechanical and thermal behaviours of plastics. In other words, the higher the viscosity, the higher the molecular weight, although the correlation is not direct. The measurement of the viscosity of polymer solutions in organic solvents gives us a value that is directly related to the molecular mass of the polymer. Analysis of recycled plastic waste and materialsĬategory: Quality control of polymers and plastic products.Biodegradability and compostability testing.Characterisation of plastics and composites.Automotive Homologations: Volkswagen Group, Renault Group, Daimler.

Laboratories accredited by EMA in accordance with ISO 17025 standard.Laboratories accredited by ENAC according to ISO 17025.Rec圜lass Certification for companies that manufacture plastic products.
#Determination of intrinsic viscosity of polymers verification
Verification of compliance with tender documents.Environmental legislation and sustainability consulting.Food Contact Materials and food safety regulations.Processing of advanced composite materials.Development and formulation of plastic materials.Advanced polymer materials & composites.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
